If you’ve ever mixed up DNA and RNA, don’t worry—most students do at first. The names are similar, both are related to genes, and textbooks love using big terms.
But once you understand their “jobs,” the dna rna difference between them becomes super clear.
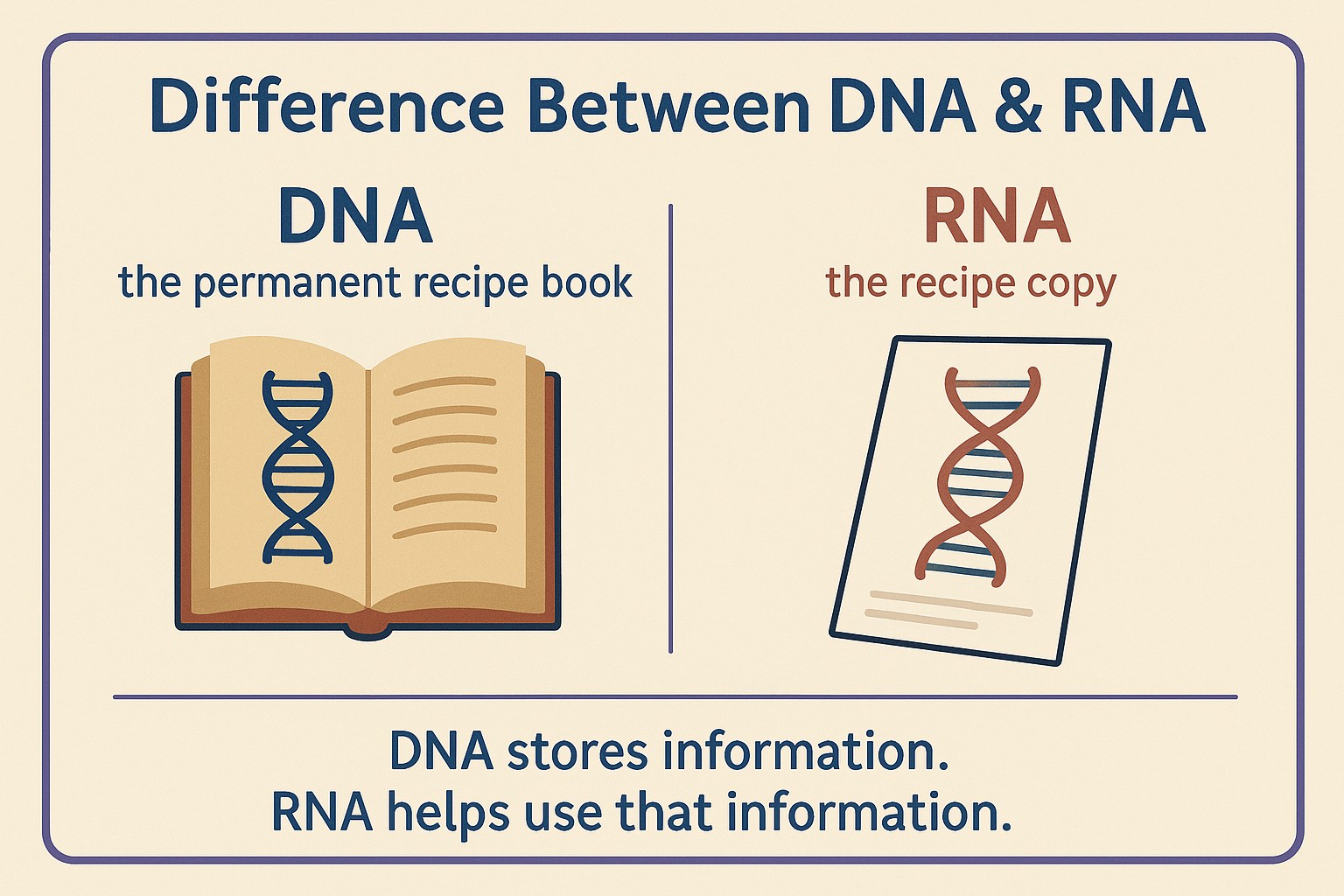
Think of it like this:
- DNA = the permanent recipe book
- RNA = the recipe copy you carry to the kitchen
That’s the heart of the difference between the DNA and RNA.
Quick idea (one line)
DNA stores information. RNA helps use that information.
This one line alone can help you answer questions like diff DNA and RNA or diff between RNA and DNA in exams.
What is DNA?
DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid. It’s the molecule that stores your genetic instructions—basically, the information needed to build and maintain an organism.
Where is DNA found?
In most organisms, DNA is mainly found in the nucleus. You’ll also find DNA in mitochondria (and in plants, chloroplasts).
What does DNA do?
DNA is like the “data storage.” It:
- Stores genetic information
- Passes information from parents to offspring
- Acts as the template for making RNA
What is RNA?
RNA stands for Ribonucleic Acid. RNA is involved in reading the DNA instructions and helping cells build proteins.
Where is RNA found?
RNA is found in the nucleus and also in the cytoplasm, especially around ribosomes (protein-making factories).
What does RNA do?
RNA is more like the “messenger + helper.” Depending on the type, RNA can:
- Carry messages from DNA (mRNA)
- Help assemble proteins (rRNA)
- Bring amino acids for protein building (tRNA)
Difference between DNA and RNA structure
A lot of marks come from structure. So if your exam asks difference between DNA and RNA structure or dna rna structure difference, focus on these:
1) Sugar
- DNA has deoxyribose sugar
- RNA has ribose sugar
2) Bases
- DNA uses A, T, G, C (Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine)
- RNA uses A, U, G, C (Uracil replaces Thymine)
3) Strands
- DNA is usually double-stranded (a twisted ladder shape)
- RNA is usually single-stranded (and can fold into shapes)
That’s the core structural difference between RNA and DNA.
10 differences between DNA and RNA (exam-friendly table)
If your teacher says, “Write any 10 differences,” this section is for you. Here are 10 differences between DNA and RNA in a clean, scoring format:
| Point | DNA | RNA |
| Full form | Deoxyribonucleic acid | Ribonucleic acid |
| Main role | Stores genetic information | Helps use genetic information |
| Sugar | Deoxyribose | Ribose |
| Bases | A, T, G, C | A, U, G, C |
| Strands | Usually double-stranded | Usually single-stranded |
| Stability | More stable | Less stable (breaks down faster) |
| Location | Mostly nucleus (also mitochondria) | Nucleus + cytoplasm |
| Types | One main form | Many types (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, etc.) |
| Length | Very long | Usually shorter |
| Copy/Use | Keeps the original instructions | Acts like working copies/helpers |
If you only need 3 differences between DNA and RNA, take the top three: sugar, base (T vs U), strand (double vs single).
Similarities between DNA and RNA
Now let’s flip the question. If your exam asks similarities between DNA and RNA or dna rna similarities, these points are safe and easy:
- Both are nucleic acids
- Both are made of nucleotides (sugar + phosphate + base)
- Both contain A, G, and C
- Both carry genetic-related information in some way
- Both are important for making proteins (directly or indirectly)
These cover most “similarities DNA and RNA” questions without overcomplicating it.
Compare and contrast DNA and RNA (simple explanation)
To compare and contrast DNA and RNA, remember: DNA is the long-term storage of genetic instructions, while RNA is the short-term worker that helps convert those instructions into proteins. DNA mostly stays protected and stable; RNA moves around more and works actively inside the cell. That’s why RNA is usually shorter, single-stranded, and less stable.
(That paragraph alone can answer: compare DNA and RNA, compare DNA from RNA, or compare and contrast DNA from RNA.)
Differentiate RNA from DNA (a quick “how to spot” guide)
If you’re asked to differentiate RNA from DNA quickly, use this checklist:
- See U (uracil)? → it’s RNA
- See double strand? → usually DNA
- Found actively near ribosomes? → commonly RNA
- Long-term information storage? → DNA
This is also a neat way to answer differentiate DNA from RNA in short form.
Difference between DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase
This is a common biology question: difference between DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase (also searched as difference between DNA and RNA polymerase).
DNA polymerase
- Makes DNA from DNA
- Used in DNA replication
- Adds nucleotides using an existing DNA template
RNA polymerase
- Makes RNA from DNA
- Used in transcription
- Produces RNA copies (like mRNA) from DNA instructions
Easy memory: DNA polymerase “copies the book,” RNA polymerase “copies a page.”
Difference between DNA & RNA virus (bonus, but useful)
You may also see questions like difference between DNA & RNA virus or difference between DNA virus and RNA virus.
- A DNA virus has DNA as its genetic material.
- An RNA virus has RNA as its genetic material.
In general (not always), RNA viruses mutate faster because RNA copying can be less stable, which is why some RNA viruses change quickly over time.
FAQ: Difference between DNA & RNA
What is the difference between DNA & RNA in the simplest words?
DNA is the storage of genetic information. RNA is the helper that reads and uses that information to make proteins.
Why does RNA have uracil instead of thymine?
RNA uses uracil (U) because it’s chemically simpler, and RNA is meant to be short-lived “working” material, not permanent storage like DNA.
Can you explain “dna rna me antar” / “dna aur rna mein antar”?
Yes—these phrases simply mean “difference between DNA and RNA” (often searched in Hindi/Urdu). The answer is the same: DNA stores info; RNA helps use it.
Is there a “difference between DNA and RNA PDF” I can use?
You can easily turn the table in this post into a one-page PDF for revision by copying it into a document and saving it as PDF (great for exams).
If my exam asks “diff between RNA and DNA,” what 3 points should I write first?
Write: (1) sugar (deoxyribose vs ribose), (2) base (T vs U), (3) strand (double vs single).
Conclusion
The difference between DNA and RNA becomes easy when you think of roles: DNA stores the original genetic instructions, while RNA helps carry and use those instructions to make proteins. Structurally, DNA is usually double-stranded with deoxyribose and thymine, while RNA is usually single-stranded with ribose and uracil. Learn the table once, and you’ll never confuse them again.
Leave a Comment