Choosing health insurance can feel like decoding a secret language—especially when you see plan types like HMO, PPO, and EPO on the same page. If you’re stuck between hmo vs ppo, you’re not alone. This is one of the most searched questions because people want a plan that’s affordable and doesn’t make getting care a headache.
Let’s make the difference between HMO and PPO super clear, with real-life examples and a simple chart.
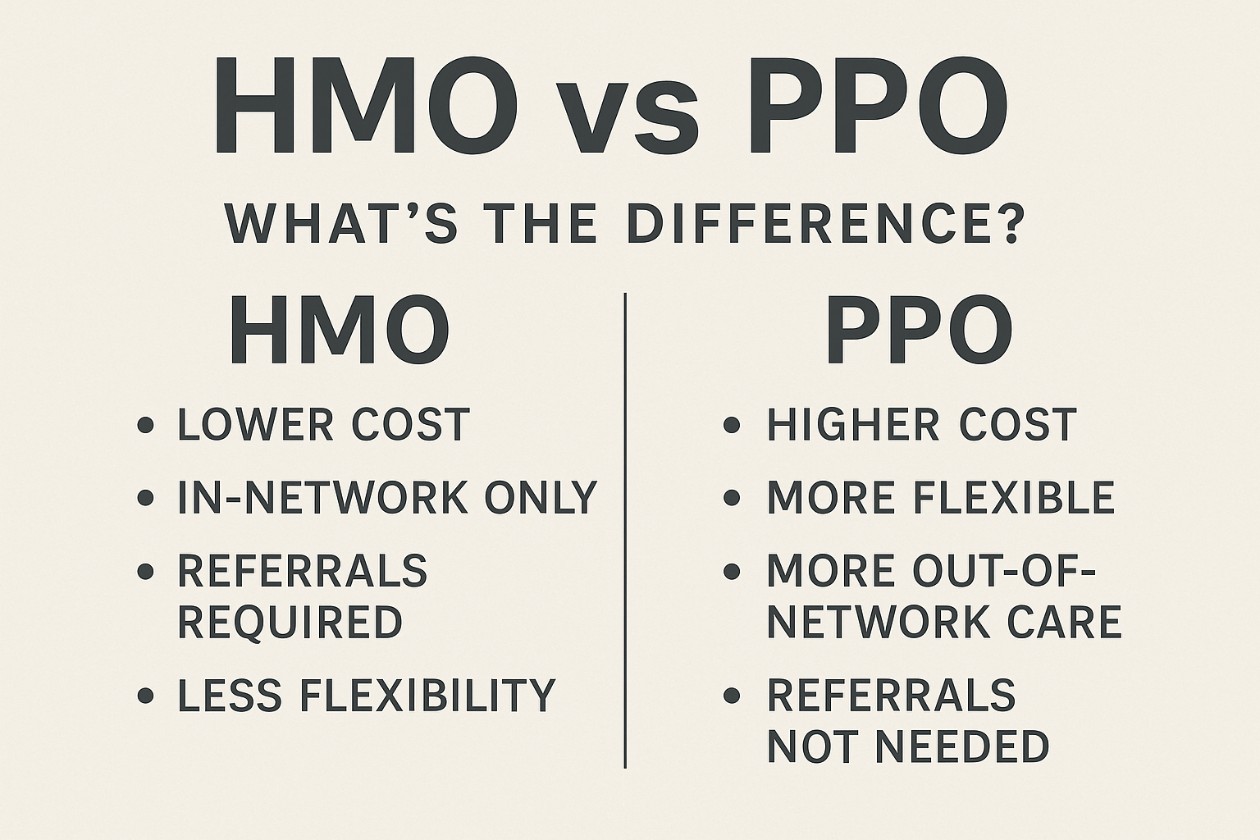
Quick answer (one line)
- HMO = lower cost, more rules (network + referrals)
- PPO = higher cost, more freedom (flexibility + out-of-network options)
That’s basically the ppo hmo difference in plain English.
What is an HMO?
An HMO (Health Maintenance Organization) usually works like a “home base” system.
How HMO plans typically work
- You pick a primary care physician (PCP)
- Your PCP coordinates your care
- You often need a referral to see a specialist
- You generally must use in-network doctors and hospitals (except true emergencies)
Why people choose an HMO
If your goal is predictable care and lower monthly cost, HMO plans can be attractive.
What is a PPO?
A PPO (Preferred Provider Organization) is built for flexibility.
How PPO plans typically work
- You can usually see specialists without a referral
- You still have a network, but you may get some coverage out-of-network
- You have more choice in doctors and hospitals
Why people choose a PPO
If you want options—especially if you travel, have preferred specialists, or don’t want referral steps—PPO plans are often easier to live with.
Difference between HMO and PPO (simple comparison chart)
Here’s a clean hmo vs ppo chart you can use to decide quickly:
| Feature | HMO | PPO |
| Monthly premium | Usually lower | Usually higher |
| Network rules | Mostly in-network only | In-network preferred, out-of-network possible |
| PCP required | Often yes | Not usually required |
| Specialist referrals | Often required | Often not required |
| Out-of-network coverage | Rare (except emergencies) | Often available (higher cost) |
| Best for | Budget + routine care | Flexibility + choice |
This table answers most versions of: difference between hmo ppo, difference between hmo and a ppo, and what is the difference between hmo and ppo.
HMO vs PPO insurance: which one saves money?
This is where the decision becomes personal.
HMO: usually cheaper upfront
HMO plans often have:
- Lower monthly premiums
- Potentially lower predictable costs (depending on plan design)
But the trade-off is flexibility: you may feel “locked in” to the network and referral system.
PPO: usually costs more, but gives options
PPO plans often have:
- Higher premiums
- Higher out-of-pocket costs for out-of-network care
- More convenience and provider choice
So the difference in PPO and HMO isn’t just money—it’s what you’re paying for: freedom vs structure.
Real-life examples (so it actually makes sense)
Example 1: HMO makes sense
You mostly see:
- a primary doctor,
- the occasional urgent care visit,
- maybe one or two specialists a year.
You don’t mind referrals, and your favorite hospitals/doctors are in-network. In this situation, HMO vs PPO often favors the HMO.
Example 2: PPO makes sense
You:
- already have a specialist you trust,
- travel often,
- want the ability to book specialist appointments directly,
- or need out-of-network flexibility.
Here, ppo versus hmo often favors the PPO.
EPO vs HMO (quick mini-section)
Because you included epo vs hmo, here’s the short version:
- EPO (Exclusive Provider Organization) usually acts like “PPO-style access” (often no referrals) but “HMO-style network limits” (in-network only except emergencies).
- HMO often requires a PCP and referrals, and is also typically in-network only.
So if you’re comparing hmo vs epo vs ppo:
- HMO = structured + referrals
- EPO = less referral hassle, still network-limited
- PPO = most flexible, usually most expensive
Dental HMO vs Dental PPO (very common confusion)
Dental HMO vs dental PPO works similarly:
- Dental HMO: lower cost, must use the network, may need assigned dentist
- Dental PPO: higher cost, more choice, may allow out-of-network (varies)
Dental plans can have different rules than medical plans, so always check the provider list and covered services.
PPO vs HMO POS (what does POS mean?)
You mentioned ppo vs hmo pos — POS stands for Point of Service.
A POS plan is often a blend:
- Like an HMO: you may need a PCP and referrals
- Like a PPO: you may have limited out-of-network coverage (often with referrals)
It can be a middle ground if you want some flexibility without full PPO cost.
FAQ: HMO vs PPO
What’s the difference between HMO and PPO?
The difference between HMO and PPO is mainly rules vs flexibility: HMOs often require in-network care and referrals; PPOs usually allow more freedom, including specialist visits without referrals and sometimes out-of-network options.
What is HMO vs PPO—what should I pick?
Pick HMO if you want lower costs and don’t mind referrals/network rules. Pick PPO if you want choice, travel flexibility, and easier specialist access.
What’s the difference between HMO & PPO for specialists?
HMOs often require a PCP referral to see specialists. PPOs often let you book specialist appointments directly.
What’s the difference between an HMO and a PPO if I go out-of-network?
With an HMO, out-of-network is usually not covered (except emergencies). With a PPO, you may still have coverage, but you’ll likely pay more.
Conclusion
The hmo vs ppo decision comes down to one trade-off: HMO is usually cheaper but stricter, while PPO is usually more flexible but costs more. If you like a guided system with predictable routine care, HMO can be a great fit. If you want freedom to choose specialists and sometimes go out-of-network, PPO is often worth the extra cost.
Leave a Comment