If biology ever made you feel like you’re memorizing words without actually understanding them, mitosis and meiosis are usually the main suspects. They sound almost the same, they both involve cell division, and yet exam questions treat them like two totally different worlds.
So let’s fix that.
In this post, you’ll learn the difference between mitosis and meiosis in a way that feels clear and memorable—plus a quick comparison between mitosis and meiosis, an easy table, and the exact “3 differences” and “ten differences” style answers teachers love.
Quick Key Takeaways (For Fast Revision)
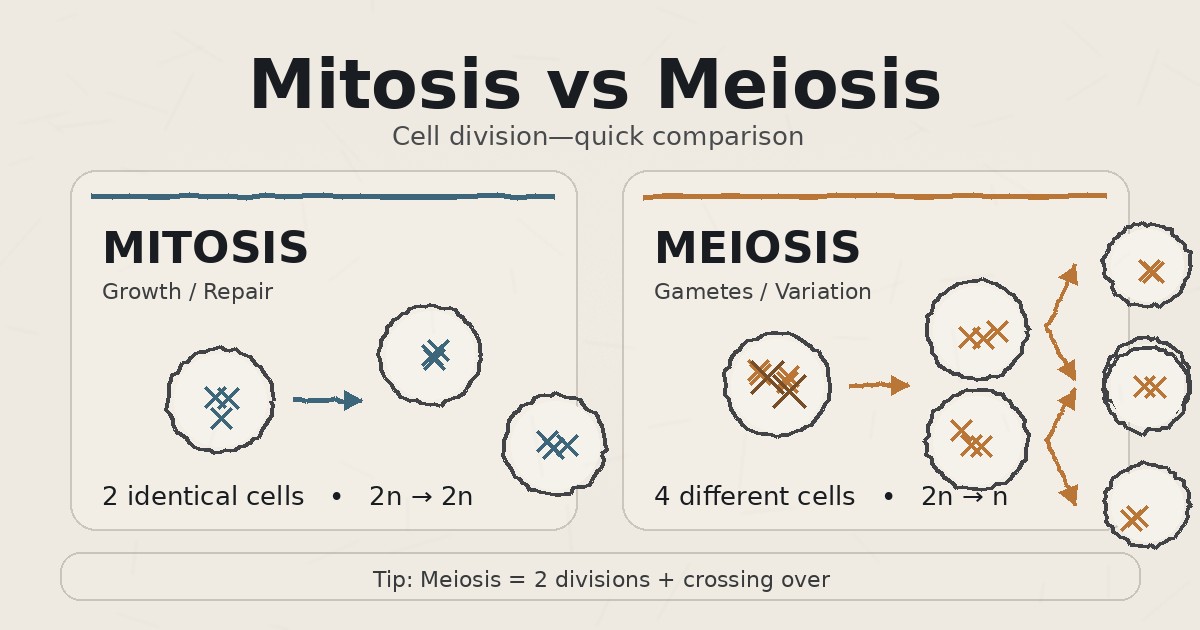
- Mitosis makes 2 identical body cells (growth/repair).
- Meiosis makes 4 different sex cells (reproduction/variation).
- Meiosis has two divisions and includes crossing over (variation).
What Is Mitosis?
Mitosis is the type of cell division your body uses to make new somatic (body) cells.
Why mitosis happens
- Growth (from baby to adult)
- Repair (healing wounds)
- Replacement (old cells like skin cells)
What mitosis produces
- 2 daughter cells
- Genetically identical to the parent cell
- Same chromosome number (Humans: 46 → 46)
If you want a simple feeling for it:
Mitosis is like photocopying a document—same content, same number of pages.
What Is Meiosis?
Meiosis is the type of cell division used to make gametes (sex cells): sperm and egg cells.
Why meiosis happens
- Sexual reproduction
- Creating genetic variation (so offspring aren’t identical)
What meiosis produces
- 4 daughter cells
- Genetically different
- Half the chromosome number (Humans: 46 → 23)
Meiosis feels more like shuffling and splitting a deck of cards—you don’t get identical copies.
Meiosis and Mitosis Difference (Big Picture)
The simplest meiosis and mitosis difference is purpose:
- Mitosis → growth and repair (same cells)
- Meiosis → reproduction (different cells, half chromosomes)
This big-purpose difference is the foundation of every other meiosis mitosis difference you’ll see.
Difference Between Mitosis and Meiosis Table
Here’s a clean difference between mitosis and meiosis table (perfect for quick exam revision):
| Feature | Mitosis | Meiosis |
|---|---|---|
| Main purpose | Growth, repair | Gamete formation (reproduction) |
| Occurs in | Body (somatic) cells | Germ cells (ovary/testis) |
| Number of divisions | 1 | 2 (Meiosis I & II) |
| Daughter cells | 2 | 4 |
| Chromosome number | Same (2n → 2n) | Half (2n → n) |
| Genetic similarity | Identical | Different |
| Crossing over | No | Yes (Prophase I) |
| Variation | Low | High |
| What separates first | Sister chromatids | Homologous chromosomes (Meiosis I) |
If your question says “write a comparison of meiosis and mitosis,” this table alone gives you a strong structured answer.
3 Differences Between Mitosis and Meiosis (Short Exam Answer)
If the question is: “Write 3 differences between mitosis and meiosis,” write this:
- Divisions: Mitosis has 1 division, meiosis has 2.
- Cells formed: Mitosis forms 2 cells, meiosis forms 4 cells.
- Genetics: Mitosis cells are identical, meiosis cells are different.
Clean, short, high-scoring.
Ten Difference Between Mitosis and Meiosis (Exam-Friendly)
Here’s a solid “ten difference between mitosis and meiosis” list:
- Purpose: growth/repair vs reproduction
- Location: somatic cells vs germ cells
- Divisions: 1 vs 2
- Daughter cells: 2 vs 4
- Chromosome number: same vs half
- Genetic identity: identical vs varied
- Synapsis (pairing): absent vs present (Meiosis I)
- Crossing over: absent vs present
- Variation: low vs high
- Separation: sister chromatids vs homologous first (Meiosis I)
20 Differences Between Mitosis and Meiosis (For Full Marks)
If you’re asked for 20 differences between mitosis and meiosis, use these (you can pick 10–15 depending on marks):
- Growth/repair vs gamete formation
- Somatic vs germ cells
- One division vs two divisions
- Two cells vs four cells
- Diploid maintained vs haploid produced
- Daughter cells identical vs non-identical
- No synapsis vs synapsis occurs
- No tetrads vs tetrads form
- No crossing over vs crossing over occurs
- Minimal recombination vs recombination occurs
- Chromosomes line up singly vs homologous pairs line up in Meiosis I
- Sister chromatids separate in mitosis vs homologous separate first in meiosis
- Anaphase: chromatids separate vs Meiosis I: homologous separate
- Helps tissue regeneration vs supports sexual reproduction
- Maintains chromosome number vs reduces chromosome number
- Produces clones-like copies vs produces unique gametes
- Happens widely in body tissues vs limited to reproductive organs
- Genetic variation not the goal vs genetic variation is a key goal
- Independent assortment not relevant vs independent assortment occurs
- Results mainly affect the individual vs affects next generation through offspring
This is a strong long-form comparison between mitosis and meiosis answer.
Similarities Between Meiosis and Mitosis
Now for the part many people forget: the similarities between meiosis and mitosis.
Similarities of meiosis and mitosis
- Both are forms of cell division
- Both occur after DNA replication (in interphase)
- Both include stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
- Both use spindle fibers to move chromosomes
- Both ensure genetic material gets into new cells
So when a question asks for the difference and similarities between mitosis and meiosis, you can confidently write both sides.
How to Distinguish Between Mitosis and Meiosis (Quick Memory Trick)
If you want to distinguish between mitosis and meiosis fast, remember:
- Mitosis = “make more of the same” (same cells)
- Meiosis = “make sex cells + variation” (different cells)
It’s simple, but it works.
About “Difference Between Mitosis and Meiosis PDF” (Quick Tip)
Many students search difference between mitosis and meiosis pdf because they want a printable revision sheet.
A smart blog upgrade is to create a one-page PDF that includes:
- the comparison table
- 3 differences
- 10 differences
- similarities
That kind of download often improves time-on-page and shares.
FAQ
1) What is the difference between mitosis and meiosis in one line?
The difference between mitosis and meiosis is that mitosis makes two identical body cells, while meiosis makes four genetically different sex cells with half the chromosomes.
2) Can you explain the differences between meiosis and mitosis simply?
Yes—if you need to explain the differences between meiosis and mitosis, say: mitosis is for growth/repair and keeps chromosome number the same; meiosis is for reproduction, halves chromosome number, and creates variation.
3) What are the similarities between meiosis and mitosis?
The similarities between meiosis and mitosis include DNA replication before division, similar stages, and spindle fibers separating chromosomes.
4) What is the best “comparison of meiosis and mitosis” format for exams?
Start with definitions, add a difference between mitosis and meiosis table, then write 3 differences between mitosis and meiosis, and include the similarities of meiosis and mitosis.
5) Why does meiosis create variation but mitosis doesn’t?
Meiosis creates variation mainly because of crossing over and independent assortment, while mitosis is designed to make identical copies.
Conclusion
Once you understand the purpose, the meiosis and mitosis difference becomes straightforward: mitosis is your body’s “copy machine” for growth and repair, while meiosis is the “shuffle-and-split” process that creates sex cells and genetic variation.
For exams, the best approach is simple: use the difference between mitosis and meiosis table, write 3 differences between mitosis and meiosis, add a longer list like ten difference between mitosis and meiosis if needed, and don’t forget the similarities between meiosis and mitosis for extra marks.
Leave a Comment